

The new round of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict has reached a regional level, with skirmishes and missile exchanges between the IDF and Hezbollah along the Lebanese border. Pro-Iranian factions are launching rockets and kamikaze drones at American military bases in Syria and Iraq, while also attempting attacks on Israel from Yemen. In response, the U.S. has retaliated, deploying substantial naval forces with significant firepower to the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Peninsula.
Content
Who and opposes Israel
Israel's allies
The situation in the conflict zone
Other countries involved
Interests of Ukraine
Putin's interest
Could there be a third world war?
Who and opposes Israel
Many analysts agree that one of the goals of the Hamas attack could have been to disrupt the normalization process between Israel and Saudi Arabia. In turn, Iran, the main rival of Saudi Arabia in the Islamic world as a whole and in the Middle East in particular, poses a key challenge to Israel's security. Iran is also the primary sponsor of anti-Israeli (and anti-American) armed groups along the borders of Israel.
A ground operation in the Gaza Strip carries the risk of involvement by pro-Iranian forces in Lebanon and Syria. This, in turn, could lead to direct U.S. intervention on the side of Israel. From here, it's only a step away from transforming the local conflict into at least a regional one if Iran and its allies attempt to inflict serious damage on American bases in the Persian Gulf Arab monarchies, as well as in Syria and Iraq.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
A ground operation in the Gaza Strip carries the risk of involvement by pro-Iranian forces in Lebanon and Syria
Iran maintains allies in the form of armed groups in the Gaza Strip, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and Yemen, forming a crescent that encompasses not only Israel but also Saudi Arabia.
Despite being a Sunni Muslim movement, Hamas finds its main sponsor and military-technical partner in Shiite Iran. Across the Middle East, Iran maintains varying degrees of connections with at least fifteen (!) major armed groups. These are sometimes collectively referred to as the “Shiite International,” although this term is not entirely accurate given the inclusion of some Sunni groups. Some of the most prominent ones are:
- Lebanon – Hezbollah (Arabic: “Party of God”) emerged in the 1980s, initially representing the interests of the Shiite minority. Gradually, with support from Iran, it transformed into Lebanon's most powerful political and military force. Hezbollah is estimated to have around 100,000 fighters and approximately 150,000 rockets, including long-range variants.
- Syria – As the civil war unfolded, Hezbollah forces aligned with President Bashar al-Assad, who belongs to the Alawite religious community (considered Shiite with certain qualifications). Later, they were joined by “expeditionary” Shiite militias, formed with Iran's support. These militias include fighters from Afghanistan (Liwa Fatemiyoun), Pakistan (Liwa Zainabiyoun), and Syria itself (Liwa al-Bakir).
- Iraq – Following the downfall of Saddam Hussein's regime in 2003, Iran provided significant military and technical support to anti-American resistance forces. In 2014, the Popular Mobilization Forces were created to combat ISIS , incorporating pro-Iranian groups like Kataib Hezbollah and Asa'ib Ahl al-Haq. While assisting rebels against ISIS, Iran continued to increase its influence in the country. Notably, it was in Iraq in 2020, where the Americans eliminated General Qasem Soleimani, considered the coordinator of overseas operations for the Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
- Yemen – The movement Ansar Allah, better known as the Houthis, controls the west and north of the country, including the capital Sanaa, boasting up to 100,000 fighters. The Houthis' official slogan succinctly encapsulates their worldview: “Allah is great, death to America, death to Israel, curse the Jews, victory to Islam.” However, the main adversary of the Houthis has been Saudi Arabia, leading an international coalition since 2014 to restore the internationally recognized government of Yemen. The U.S. fleet regularly intercepts Iranian weapon shipments to the Houthis, with some recently redirected to Ukraine.
Collectively, these diverse groups under Iran's auspices are commonly referred to as the “Axis of Resistance.”
In close proximity to Israel, there are already two de facto fragmented states—Lebanon and Syria—only partially controlled by central governments. In southern Lebanon, as mentioned earlier, the pivotal role is played not by official authorities but rather by Hezbollah. In Syria, alongside pro-Iranian forces, there is American, Turkish, and Russian military presence, as well as militia from Kurdish autonomy and numerous local armed groups. The conflict in the Gaza Strip and the renewed escalation of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict as a whole pose a threat to internal stability in Jordan and Egypt, where influential pro-Iranian groups are absent. Jordan is home to over 2 million Palestinian refugees, and the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt hosts various Islamist groups, including a local branch of ISIS.
Iran warmly welcomes the terrorist attack by Hamas, although it denies direct involvement. Sources from The Wall Street Journal suggested that it was commanders of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps who assisted Hamas in developing the attack plan and gave the final approval for the assault. However, according to the assessment of the American intelligence community, Iran does not have full control over proxy forces, particularly Hezbollah.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
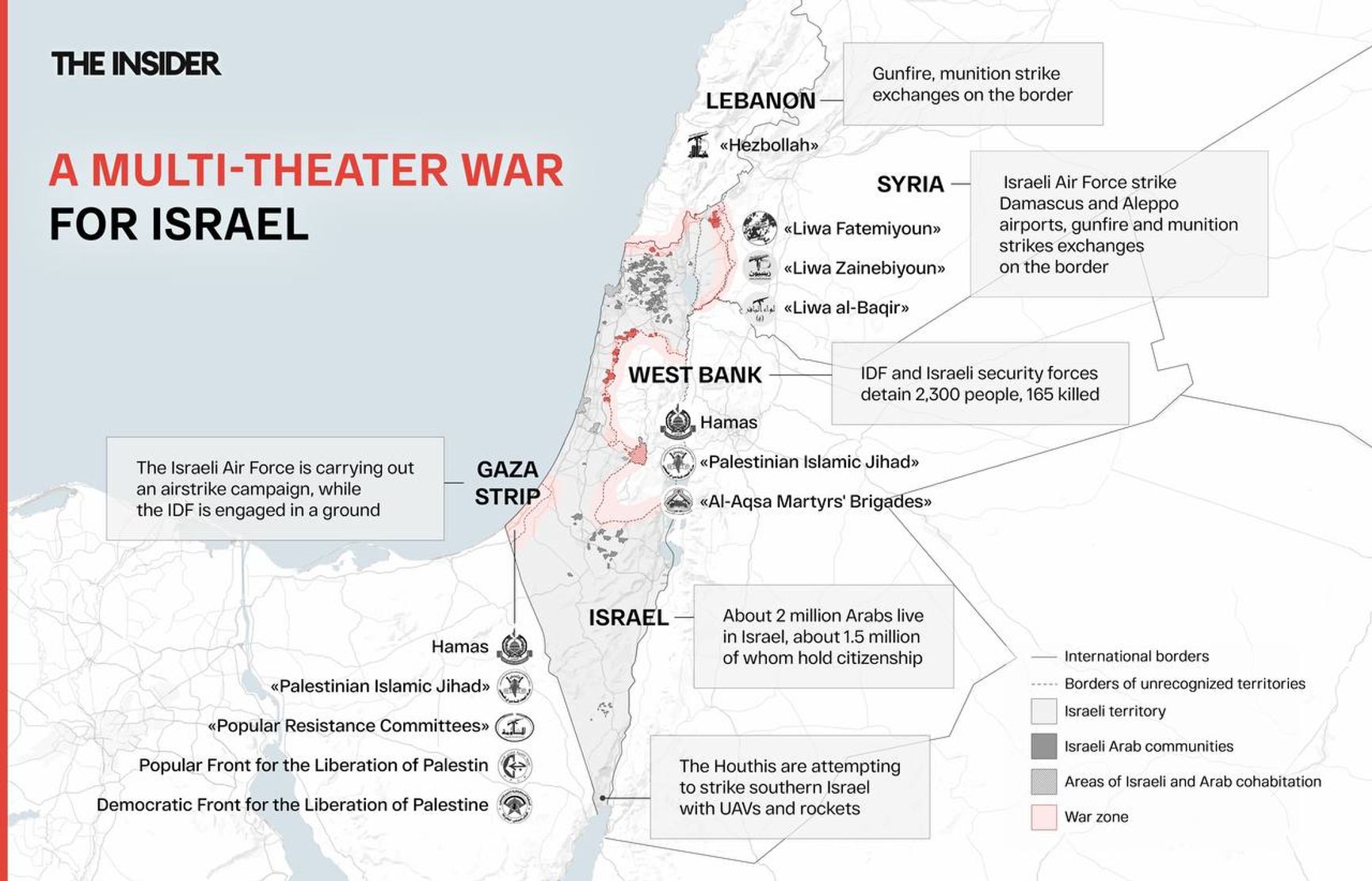
Multi-theater war for Israel
The Insider
Potentially, Israel could become entangled in a war on multiple “fronts” or “theaters of military operations” (TMOs):
- Gaza Strip
- Southern Lebanon
- Border areas of Syria
- West Bank of the Jordan River
- Arab towns and areas within Israel
Currently, the internal theater of military operations appears to be the quietest—Israeli Arabs, who previously actively supported Palestinians, have not taken to the streets, fearing a sharp and forceful response. However, if desired, other “fronts” can be added, such as the “front” of information warfare waged online and in the media, as well as clashes in the ideological space, involving different understandings of the nature of the conflict and explanations of who is right and who is to blame.
Israel's allies
The only official ally of Israel in the region is the United States. The Americans have more than 45,000 soldiers and a network of military bases in the Middle East. Training and logistics centers operate in Syria, Iraq, and Jordan, servicing small contingents engaged in counterterrorism efforts. The headquarters of the United States Central Command and the Fifth Fleet are located in Qatar and Bahrain, respectively, while Kuwait and the UAE host significant airbases. There are military advisors and technical specialists in Saudi Arabia and Oman. Finally, in Turkey, the Incirlik Air Base stores 20–30 American tactical nuclear weapons, specifically B61 nuclear bombs.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
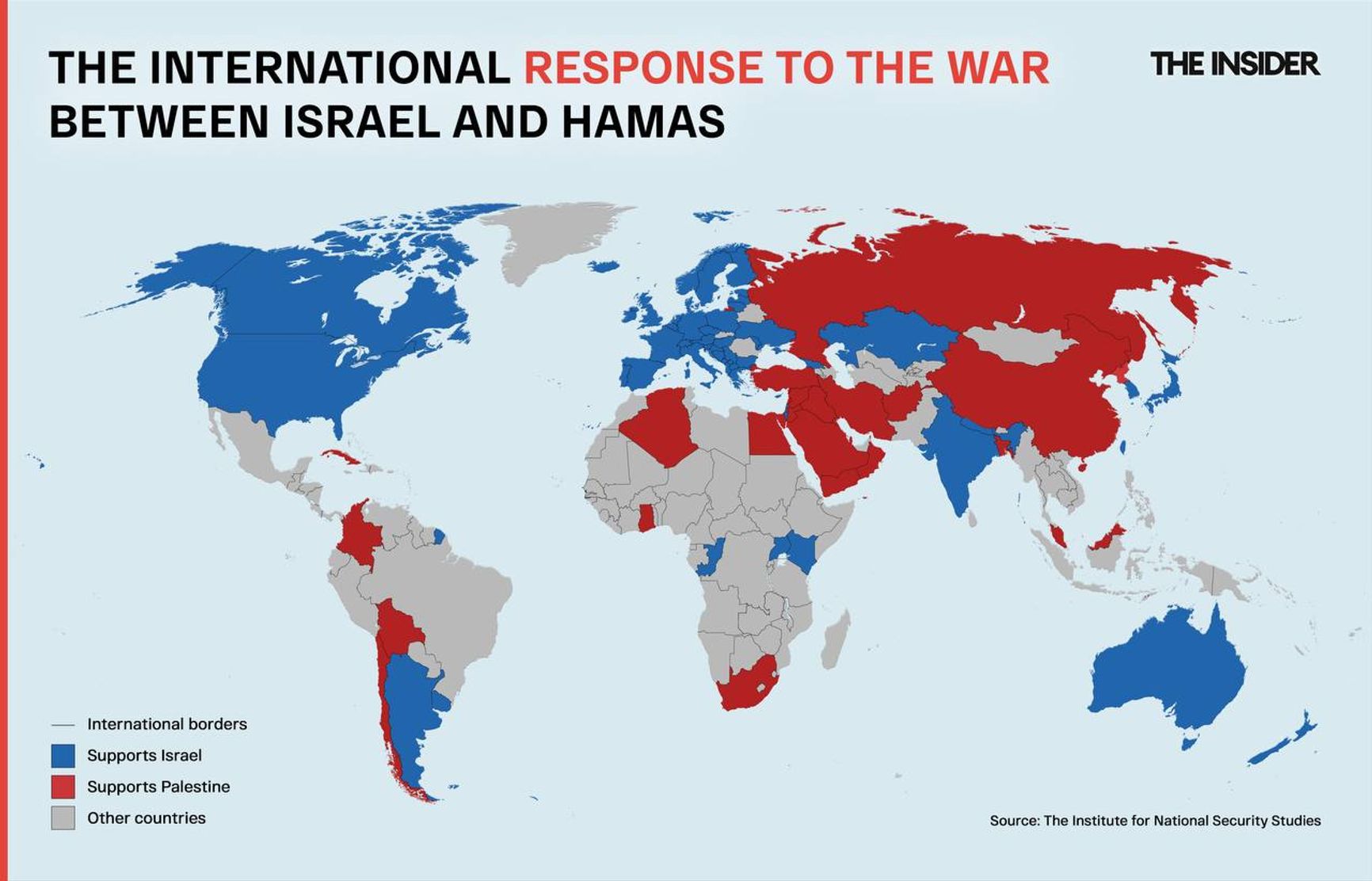
How the world is reacting to the Israel-Hamas war
The Insider
In theory, the closest allies of the U.S., such as France, the United Kingdom, and other NATO countries, could support Israel. For instance, French President Emmanuel Macron has proposed creating an international coalition to combat Hamas, similar to the one that operated against ISIS. Although Saudi Arabia has frozen the normalization process with Israel and publicly supports the Palestinians, Saudis participate in intercepting rockets launched by the Houthis and blocking incoming munitions. It's quite likely that they may eventually have to resume military actions against the Houthis in Yemen.
The situation in the conflict zone
Essentially, the conflict with Hamas and its allies has expanded beyond the Gaza Strip and the adjacent southern regions of Israel. Israeli and American military forces are engaged in combat on one side, and fighters from Hezbollah and other Shiite groups are involved on the other.
The IDF are conducting a ground operation in the northern part of the Gaza Strip, exchanging fire on the Lebanese border, and carrying out military-police raids in the West Bank. Additionally, strikes are being launched on airports in Syria. Airports in Aleppo and Damascus have been bombed several times to hinder the transfer of military supplies and personnel from Iran in case it decides to enter the war.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
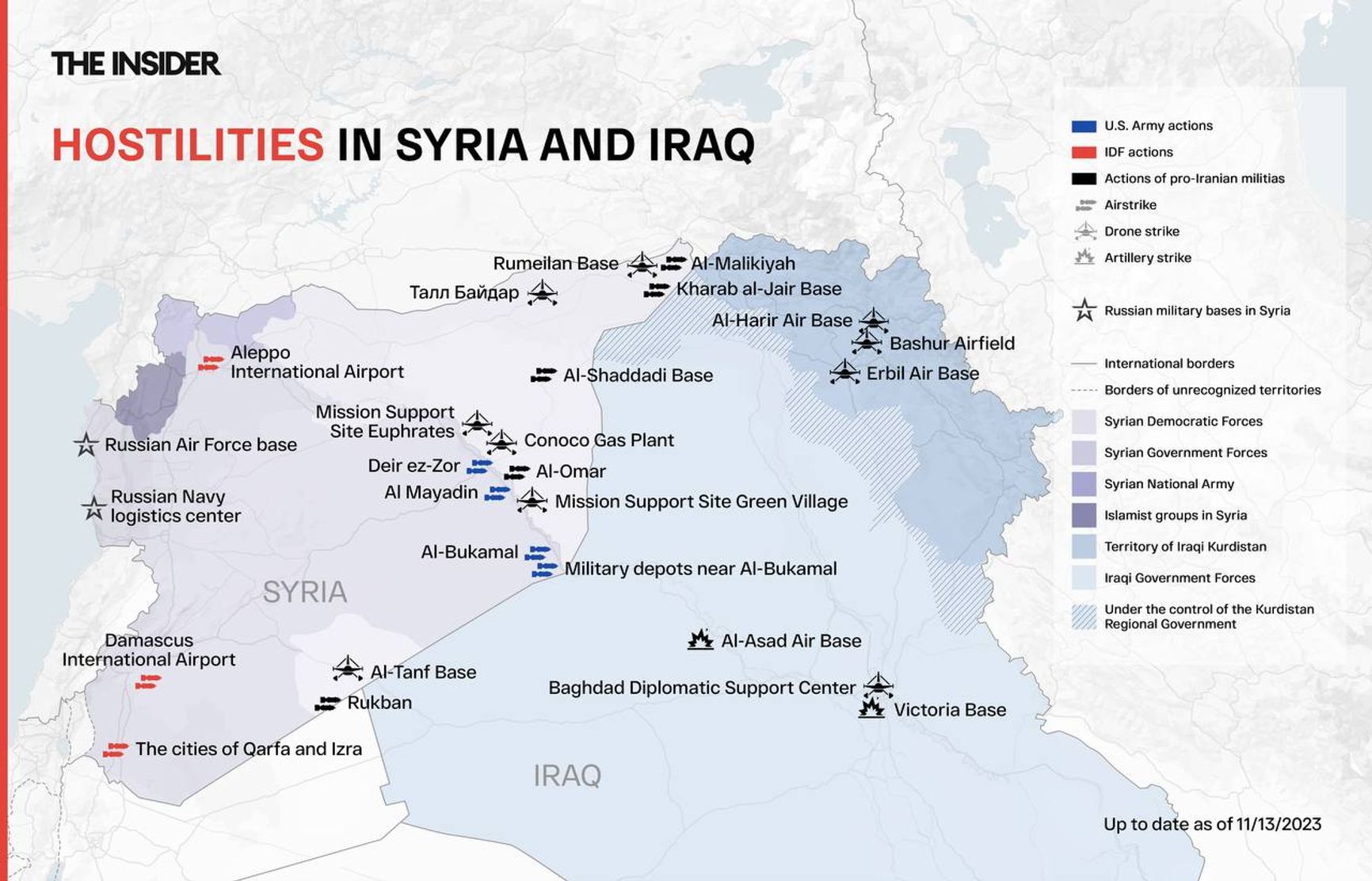
Combat operations in Syria and Iraq
The Insider
Pro-Iranian formations regularly shell U.S. bases in Syria and Iraq. According to Pentagon data, since October 17, U.S. forces and the anti-ISIS coalition have been attacked at least 56 times by rockets and kamikaze drones. In just three weeks, 56 people were injured. In response, American aircraft are bombing support bases of pro-Iranian formations in eastern Syria. On the night of November 9, U.S. troops, supported by the Syrian Democratic Forces, engaged in ground combat with Assad's army.
The Houthi movement launches long-range missiles and barraging munitions at Israel from Yemen. However, these are either intercepted (including in space) or hit Egypt. In other words, the scale of the military operations already corresponds to a regional war, but the intensity, excluding the Gaza Strip operation, is not yet at that level. Until Hezbollah transitions from symbolic border skirmishes to massive missile attacks on Israel, inevitably prompting Israeli airstrikes deep into Lebanese territory, the situation is unlikely to change.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
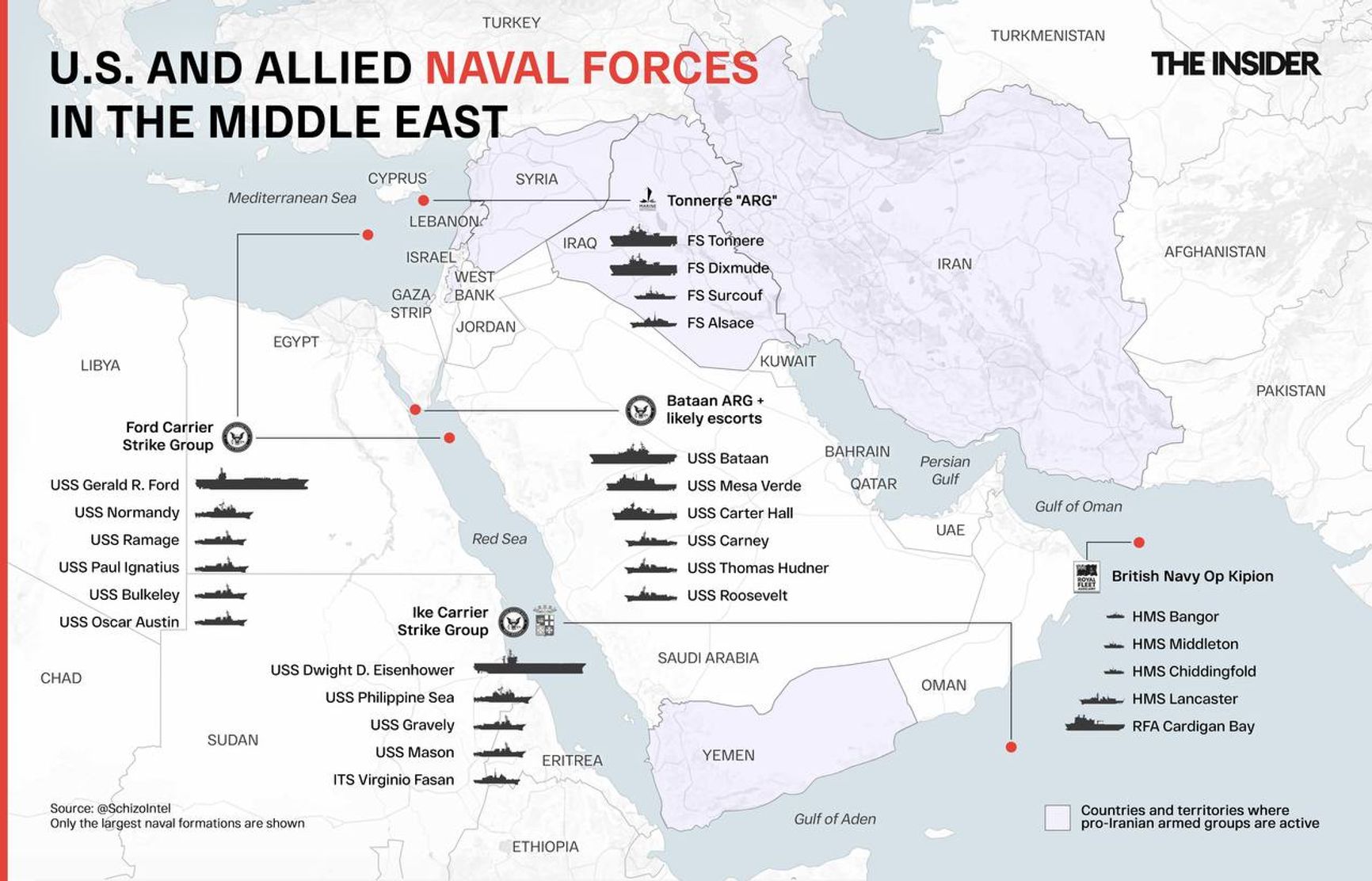
U.S. and allied naval forces within the conflict zone
The Insider
An unprecedented naval armada has emerged in the conflict zone, reminiscent of the scale not seen since World War II. Leading this formidable force is an aircraft carrier strike group commanded by the state-of-the-art aircraft carrier Gerald Ford, now stationed in the eastern Mediterranean. Simultaneously, the second aircraft carrier, the Dwight D. Eisenhower, is strategically positioned off the coast of the Arabian Peninsula. In a concerted effort, the United States and its allies are deploying advanced missile defense systems, such as THAAD and Patriot, along with additional fighter squadrons and military contingents to the Middle East. The military assembly orchestrated by the U.S. and its allies, which includes the Israeli Defense Forces, undeniably surpasses the might of Hamas and even outmatches the combined strength of all Iranian proxies in the region. However, the precise role of Iran, boasting the largest yet technologically lagging army in the area, remains uncertain within this complex equation.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
An unprecedented naval armada has emerged in the conflict zone, reminiscent of the scale not seen since World War II
It's not surprising that such a concentration of forces is associated with a potential attempt to strike Iran—the primary source of most security challenges for the U.S. and its allies in the Middle East.
Other countries involved
Following the outbreak of the war between Israel and Hamas, U.S. President Joe Biden declared the need for a new world order, directly linking Palestinian militants and Vladimir Putin:
“Hamas and Putin represent different threats, but they share this in common: both want to completely annihilate a neighboring democracy… We cannot and will not let terrorists like Hamas and tyrants like Putin win… Would-be aggressors around the world would be emboldened to try the same. The risk of conflict and chaos could spread in other parts of the world — in the Indo-Pacific, in the Middle East.”
As is well known, Vladimir Putin is also striving for a new world order. He has criticized the current one (based on rules) as colonial.
Here's how the map of recognition of the state of Israel looks in the world.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
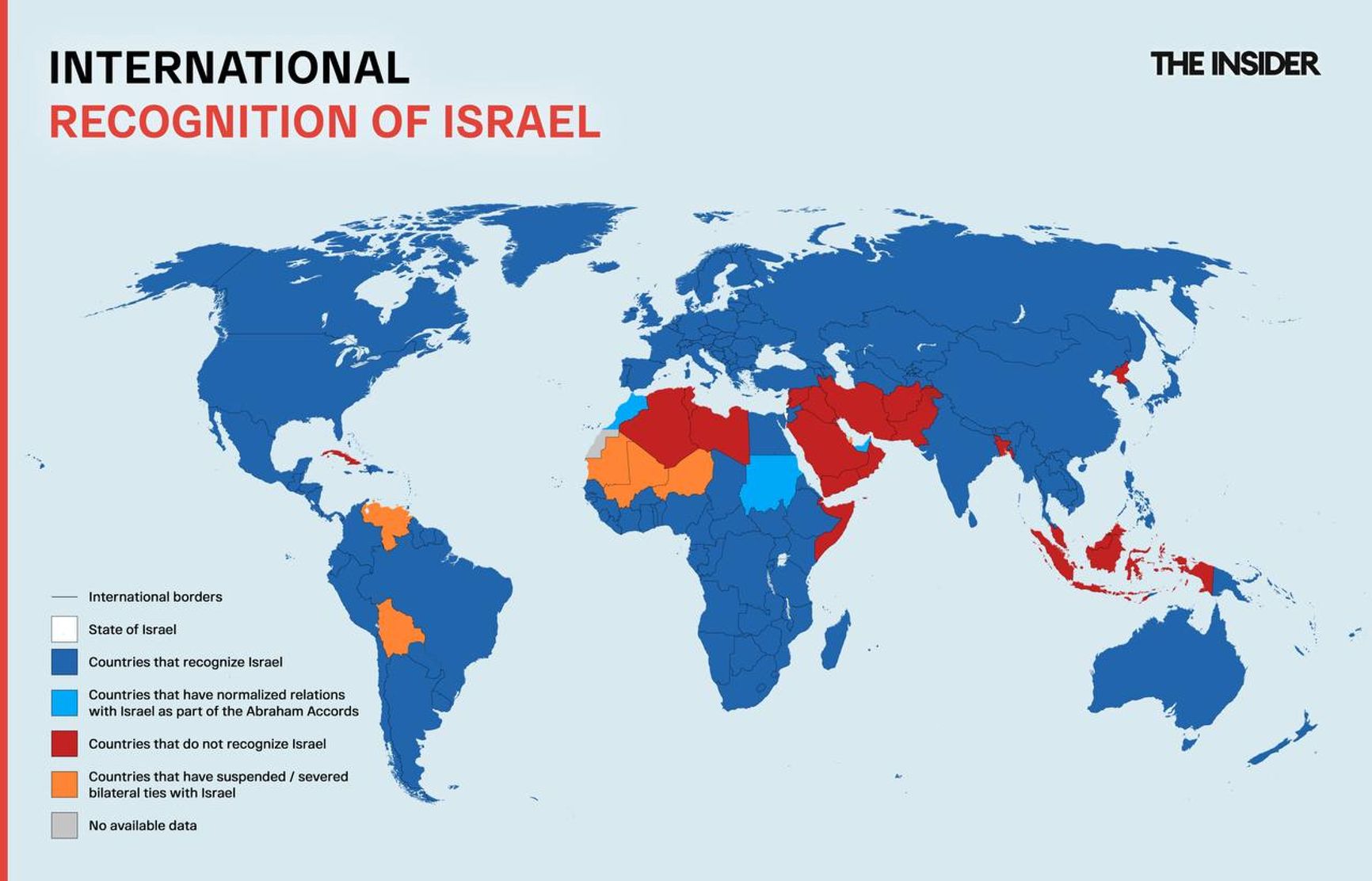
The international legal status of Israel
The Insider
Here are the countries with interests in the Middle East:
- Turkey has been implementing a “neo-Ottoman” strategy for years, aiming to regain influence in all regions of the former Ottoman Empire. President Recep Tayyip Erdogan speaks of an “upcoming battle of the Cross and the Crescent,” placing the conflict in Gaza alongside Karabakh and Libya, where success favored parties supported by Turkey (Azerbaijan and the UN-recognized Libyan government, respectively).
- Iran pursues a consistent policy of expanding influence in the Middle East, relying on Shiite armed groups under the brand of the “Islamic revolution” to push back the U.S. and ideally destroy Israel.
- The U.S. seeks to establish a lasting peace and solidify its long-term presence through alliances between Israel and its Arab allies, the Persian Gulf monarchies (the so-called Abraham Accords ).
- Russia is “returning” to the Middle East: a limited contingent of Russian forces is stationed in Syria, with an airbase and logistical support base for the fleet. Meanwhile, the Kremlin aims to dig in and set up military bases in Sudan and Libya (where Wagner Group mercenaries have been operating for a long time).
- China views the Middle East as the next target for the expansion of its Belt and Road infrastructure and investment initiative.
Interests of Ukraine
The Biden administration is working towards unifying military aid for Ukraine, Israel, and Taiwan into a comprehensive package valued at over $100 billion. Despite this, a slim majority of Republicans in the House of Representatives are planning to separate Israel's aid from that of Ukraine. In the Russian Z-sphere, there is evident delight over the prospect of resources initially allocated for Ukraine being redirected to Israel. However, it's worth noting that the types of weapons and ammunition earmarked for each country (including Taiwan) have minimal overlap.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
The types of weapons and ammunition earmarked for Israel and Ukraine have minimal overlap
For instance, the current discussion revolves around the transfer of Spice precision-guided bombs worth $320 million, for which Ukraine simply lacks carriers. The U.S. is also returning to Israel the Iron Dome batteries it previously purchased. These complexes are unsuitable for Ukraine as they cover a relatively small territory and are designed to counter less technologically advanced missiles than those possessed by Russia.
More importantly, the operation against Hamas and the relatively moderate increase in tension in the region have significantly diverted attention from the war in Ukraine. The Wall Street Journal, citing informed diplomatic sources, reports that Kyiv will likely not be able to convene a representative “peace summit” by the end of the year precisely for this reason.
The Middle Eastern conflict has substantially complicated the peace process, as Arab and developing countries have sided with the Palestinians, while Ukraine and its Western allies have supported Israel. According to The Financial Times, Russia's reputation as a violator of international law and a worthy condemner of aggression appears at least debatable amid the bombardments and a significant number of civilian casualties in the Gaza Strip.
Putin's interest
Vladimir Putin blames the United States for the escalation of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict.
“I think many will agree with me that this is a clear example of the failure of United States policy in the Middle East, as they tried to monopolize the conflict resolution but, unfortunately, were not concerned with finding compromises acceptable to both sides.”
Following this, Russian lawmakers were advised to blame Americans for everything, and the Prosecutor General's Office refused to recognize Hamas as a terrorist organization.
Primarily, in Moscow, there is an expectation that the war between Hamas and Israel will divert the attention of the United States and other Western countries from the conflict in Ukraine, limiting the volume of military aid to Kyiv. President Vladimir Putin has claimed that without Western support, Ukraine can only hold out for a week. However, the inventory of military equipment and ammunition required by the Armed Forces of Ukraine and the IDF in the conflicts they are currently engaged in shows little overlap (see above).
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
In Moscow, there is an expectation that the war between Hamas and Israel will divert the attention of the United States from the conflict in Ukraine
Over the past decade, Russia has emerged as a significant player in the Middle East. In 2015, Putin intervened in the civil war in Syria, and since then, there has been a Russian military presence in the country. Now, Moscow has been considering setting up a military-naval base in Libya, where the Kremlin supports the government of Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar in Benghazi. Moscow has also reached an agreement to establish a base in Sudan on the Red Sea.
Following the Russian intervention in Syria and the start of the war in Ukraine, Moscow forged close ties with Iran, particularly in the realm of weapon supply. In addition to Iran and pro-Iranian forces in Syria, Russian weapons have even reached Gaza. During the current escalation, as in the past, Hamas militants have used Russian Kornet anti-tank complexes. According to unconfirmed reports, Russian P-800 Yakhont anti-ship missiles made their way to the Lebanese Hezbollah through Syria.
Paradoxically, diplomatic ties with Israel also saw an enhancement during this time. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu underscored his personal rapport with Putin in the 2019 election campaign, likely as a strategy to appeal to the Russian-speaking voters. The practical collaboration during the Syrian war allowed Russian aircraft to bomb southern Syria while freely maneuvering over the Golan Heights, which are under Israeli jurisdiction. Russian air defenses in Syria did not obstruct Israeli airstrikes on pro-Iranian targets. Even incidents like the downing of a Russian reconnaissance plane, the Il-20, by Syrian air defenses while countering an Israeli air raid, did not impede the cooperation.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
Russia managed to maintain relations with Israel despite its close cooperation with Iran
With the onset of the full-scale Russo-Ukrainian war, Israel refrained from providing military assistance to Kyiv.
Recently, however, Israel's understanding with the Kremlin seems to have been strained, especially after an official delegation from Hamas visited Russia. Apart from sharp remarks from Amir Weitman of the ruling Likud party directed at Russia on RT, Israel has stopped notifying Russia about airstrikes on Syrian territory.
Surprisingly, the escalation of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict has become a factor in domestic politics, at least in the North Caucasus, where several anti-Israeli actions occurred, and a Jewish pogrom, unprecedented in decades, was narrowly averted.
Another less obvious aspect is the impact of the major conflict on energy markets. Israel, for instance, halted gas production in its largest Mediterranean field for security reasons. Coupled with news of damage to the gas pipeline between Finland and Estonia, this immediately led to a 30% increase in gas futures prices. If the escalation reaches a war with Iran, energy prices will undoubtedly experience a long-term rally, filling the Russian budget with additional revenue. However, as of now, oil price dynamics do not align with these forecasts.
Could there be a third world war?
The conflict between Israel and the Hamas movement is embedded in a broader context of alliances that have evolved during the Russia-Ukraine war. The United States and Western allies of Ukraine, including the official government in Kyiv, support Israel, while Russia's allies like Iran and North Korea assist Hamas. In other words, major powers align on opposing sides in an increasing number of armed conflicts in different regions of the world. The United States finds itself face-to-face with four significant adversaries: Russia, Iran, North Korea, and China, posing the most serious foreign policy challenge for America since at least the Korean War.
Furthermore, Israel's war against Hamas is perceived as a new point of tension in a series of conflicts sparked by blows to the world order, such as the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and the full-scale aggression against Ukraine in 2022. These events were followed by Azerbaijan's forceful resolution of the Nagorno-Karabakh issue. Notably, in all three cases, the West failed to assert its interests, likely serving as a stimulus to challenge the status quo in other parts of the world. Many experts draw the conclusion that the Western world, led by the U.S., is losing its ground, providing “rising powers” like China, Iran, or Russia an opportunity to challenge it— this is roughly how the mechanism behind the emergence of wars, known as the “Thucydides Trap”, is described in the most general sense.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.
“Rising powers” like China, Iran, or Russia are provided with an opportunity to challenge the U.S. and the entire world order
The successful retention of power by Assad in Syria, the annexation of Crimea by Russia, and the subsequent war against Ukraine, coupled with the expansion of Iranian proxies in the Middle East, are perceived as links in a chain reflecting the failure of Western deterrence policies. From this perspective, following Russia and Iran, China is expected to take action in an attempt to regain control over Taiwan. This pattern is reminiscent of the series of local conflicts in the Balkans and North Africa in the early 20th century that culminated in the outbreak of World War I, driven by the inability to maintain a balance of power in Europe.
The subsequent World War II was preceded by the Japanese occupation of Manchuria, the war with China, the fascist Italian conquest of Ethiopia, the Spanish Civil War, and the Nazi German expansion in Europe. In each case, Western democracies proved incapable of guaranteeing the status quo established after World War I, and the League of Nations, created to maintain peace, demonstrated its ineffectiveness.
However, the likelihood of a global, rather than a regional, conflict remains relatively low.
Currently, Iran sends conflicting signals, and uncertainty prevails regarding the intentions and plans of pro-Iranian forces in Syria and Lebanon. Notably, there is uncertainty surrounding the expectations of specific actions against Israel, as demonstrated by Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah's speech that failed to materialize concrete actions. Bloomberg Economics analysts have modeled three scenarios for the situation's further development, considering direct confrontation with Iran as the least likely. Most importantly, accumulated knowledge about wars throughout human history unequivocally indicates that large-scale wars typically either involve numerous participants for a short period or remain limited in scale.
Furthermore, a leaked set of secret documents from U.S. intelligence in February included an assessment of the low probability of escalation between Israel and Hezbollah. This is because, due to several objective factors, both sides prefer a position of demonstrating strength and ensuring mutual deterrence without entering into open conflict. Iran is likely to adopt a similar strategy, as it lacks the resources for war against Israel and, even more so, the United States.
ISIS or ISIL – the «Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant», later known as the «Islamic State» (IS), was an Islamic radical terrorist movement that, from 2014 to 2017, held significant portions of territory in Syria and Iraq.
«הצה»ל» («Tzahal» in Hebrew), which stands for «Israel Defense Forces»
«The Abraham Accords» are agreements on the normalization of relations with Israel, signed in 2020 with the support of the United States, involving Arab countries such as the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. In 2021, Sudan also joined these agreements.